Community Tip - If community subscription notifications are filling up your inbox you can set up a daily digest and get all your notifications in a single email. X
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
An Arrow above a function?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
An Arrow above a function?
Hello,
This may appear to be a stupid question but I saw this in the built in help and did not know how to enter it into my file.
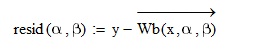
This arrow above the function. How do I enter it?
and above all why is it there? What does it do?
Thank you
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Other
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
In the minerr quicksheet example x and y are a vector of values. So the function has been vectorized so each value of x and y are passed to the function inturn.
Mike
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Its called the Vectorize operator and can be founf on the Matrix tooler
Description from the help menu:-The vectorized product returns an array of the same size as A and B in which each element contains the product of the paired elements of A and B. The non-vectorized product performs a standard matrix multiplication.
Simple example below.
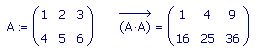
This is a very useful function and is constantly used by forum members.
Mike
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Thank you for the helpful reply. I now understand the concept of the vectorize operator and it is easy to see it from your example but why use it in the screenshot I provided?
its not vector multiplication? So why is the vectorize operator used there? and what would happen without it?
BTW the screenshot is from the minerr quicksheet
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Its doesn't have to be used on a vector mulitiplication, look below.

The above retuens an array. 1 if the element in row is not zero, a zero is returned otherwise.
Mike
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
In the minerr quicksheet example x and y are a vector of values. So the function has been vectorized so each value of x and y are passed to the function inturn.
Mike
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
k got it. Thanks for the explanation ![]()
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
A few additional notes.
Mathcad will implicitly vectorize trigonometric, logarithmic, Bessel and probability distribution functions when a vector is passed as an argument.
It will also implicitly vectorize vector arguments when the factorial, square and nth root, exponentiation and any relational operators are applied.
However, the vectorize operator must still be applied for all functions and operators in the case of a matrix argument.
Mike





