Community Tip - Learn all about the Community Ranking System, a fun gamification element of the PTC Community. X
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Study 5. "Cloud" thermal engineering algorithms
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Study 5. "Cloud" thermal engineering algorithms
This study explains how cloud algorithms can be used in the heat power processes calculations for the thermal power plants, for example, the processes of expansion or throttling of the steam, compression water in the pump. Information technology for the Internet libraries of equations is provided.
Mathcad and Excel sheets of the Study in attach
Add Information!
On the site Interactive Equations - Knovel
now (up 2015/09/25) we can use 50 sheets with properties of water and steam
You can download sheets of figures:
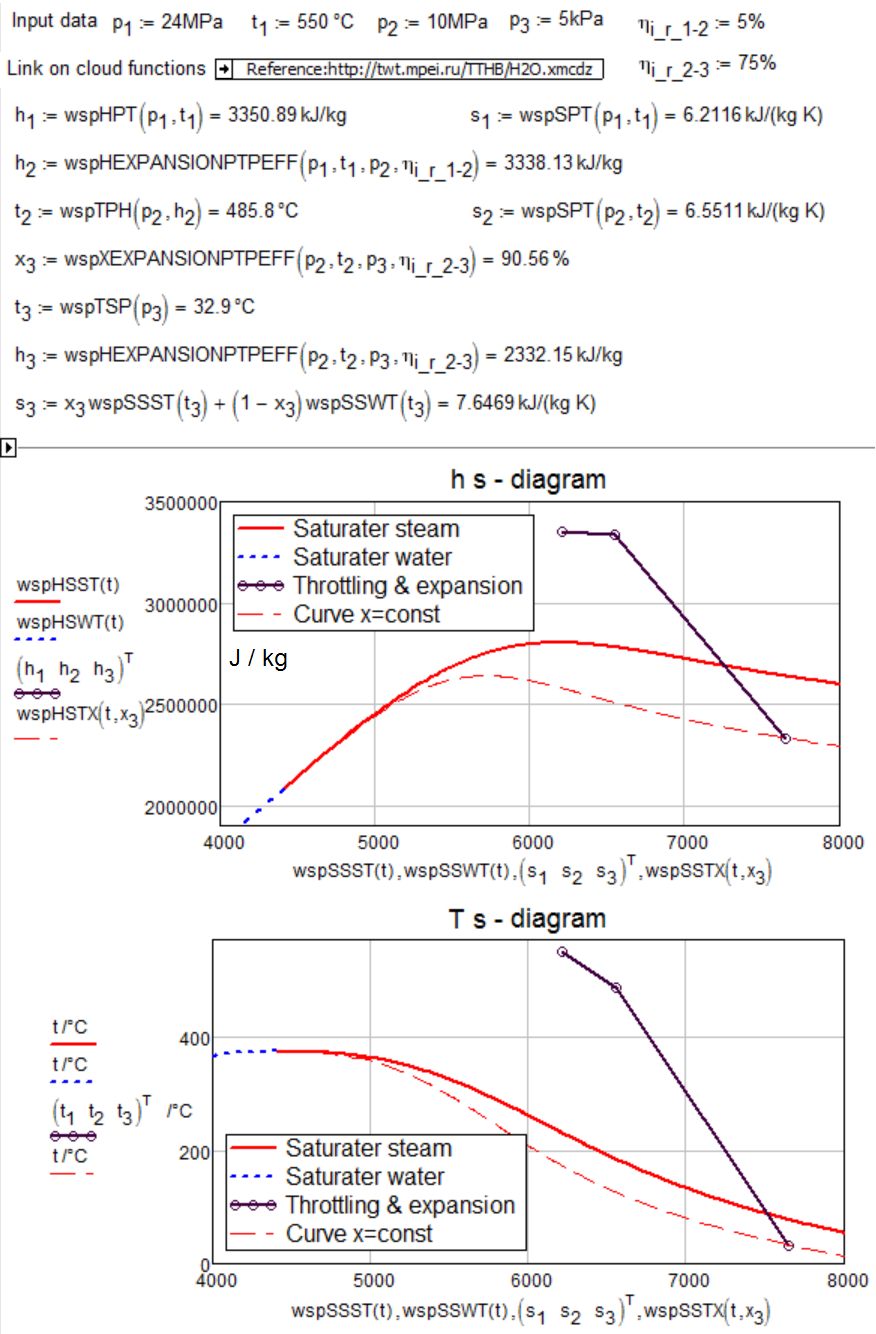
Fig. 5.1. Calculation Process throttling and expansion of steam in the turbine
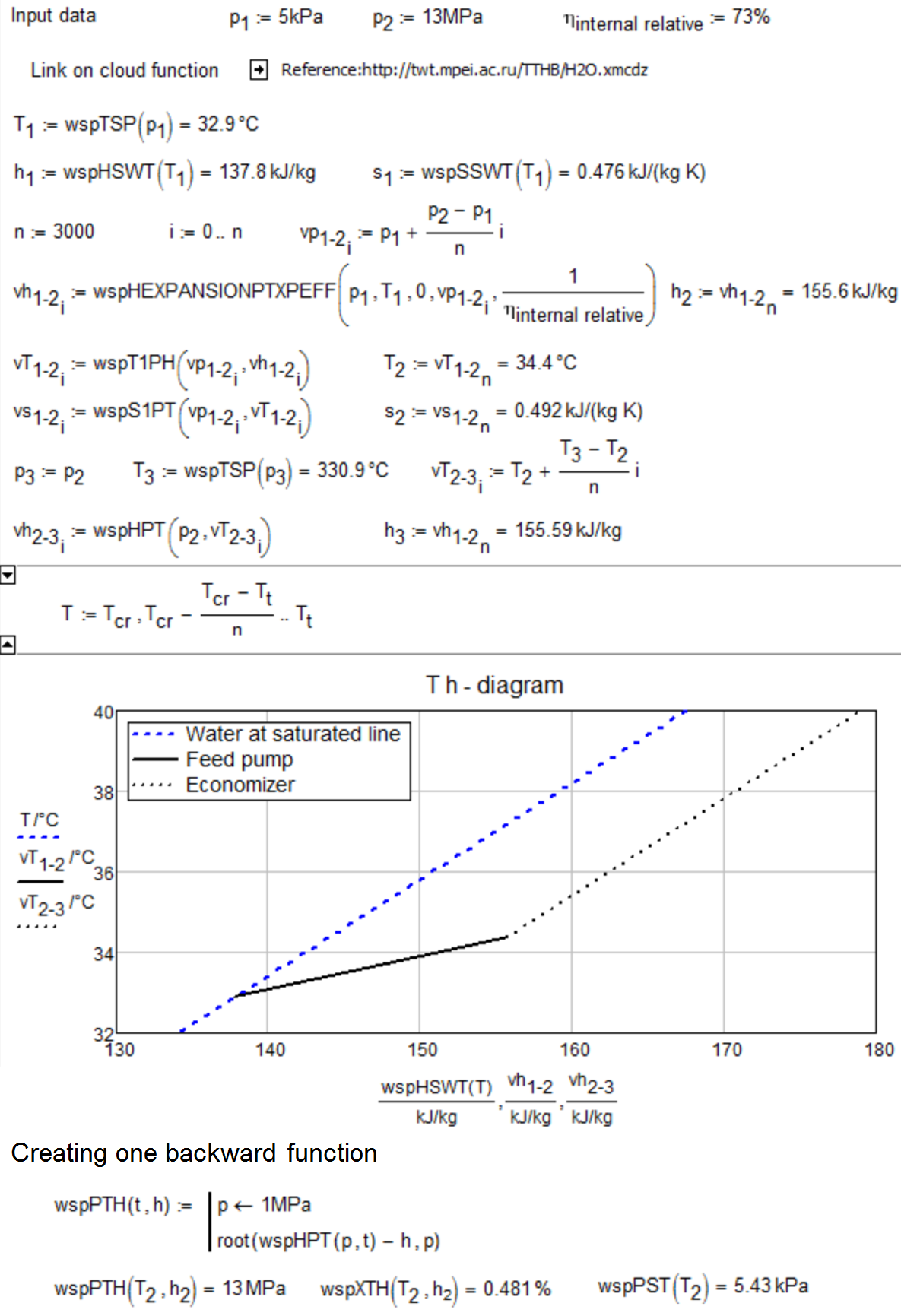
Fig. 5.2. Pump performance calculation
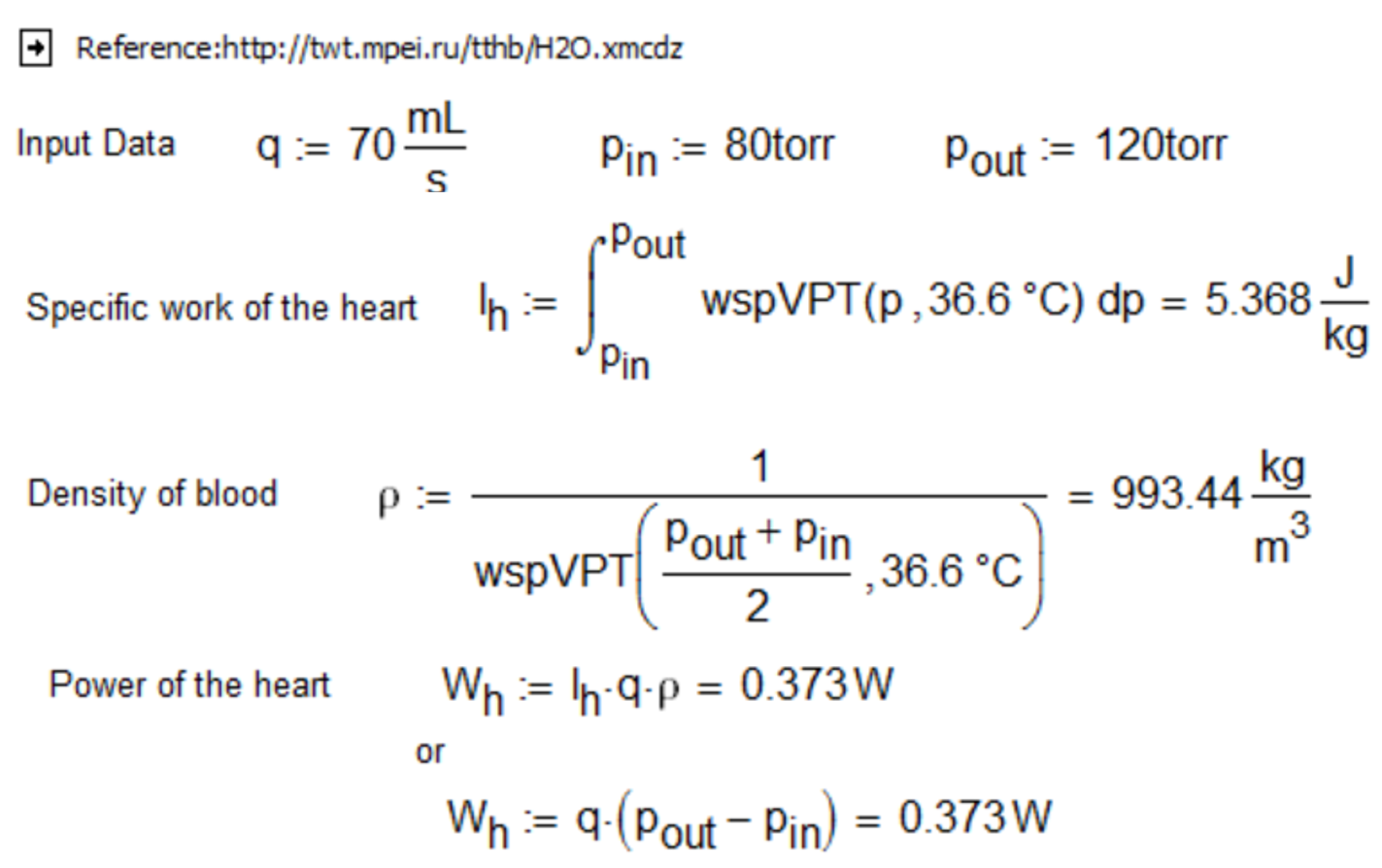
Fig. 5.3. Thermodynamic parameters of a human heart
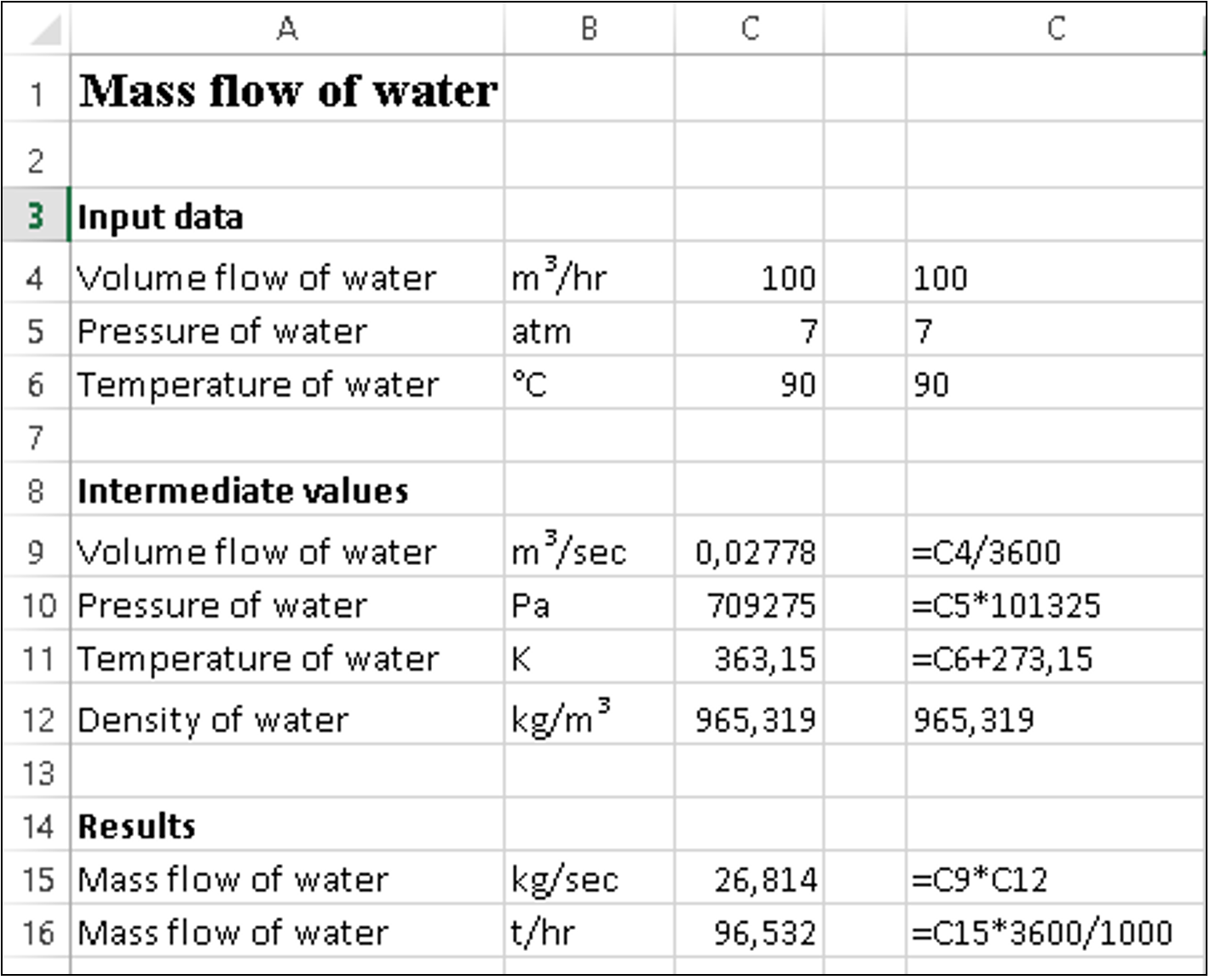
Fig. 5.4. Calculation of water mass flow in MS Excel (demonstration of calculated values and formulas used; work with connected WaterSteamPro package)

Fig. 5.5. Calculation of water flow rate in Mathcad: usage of a reference to a "cloud" function

Fig. 5.6. Calculation of water mass flow rate in SMath: operation with a function in hidden area
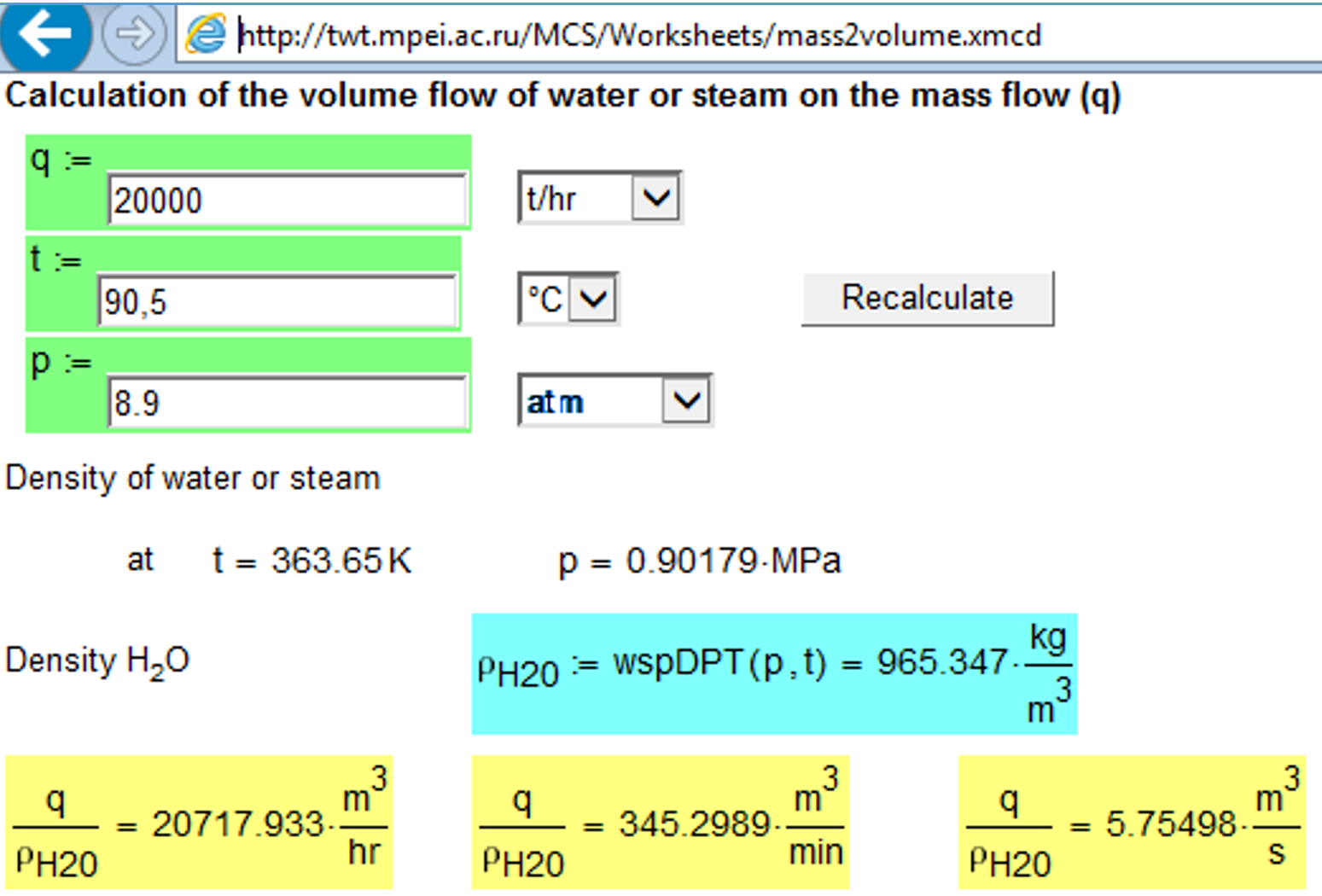
Fig. 5.7. Network calculation of water flow rate (a task which is inverse to the ones shown in Figs. 5.4–5.6) - http://twt.mpei.ac.ru/MCS/Worksheets/mass2volume.xmcd
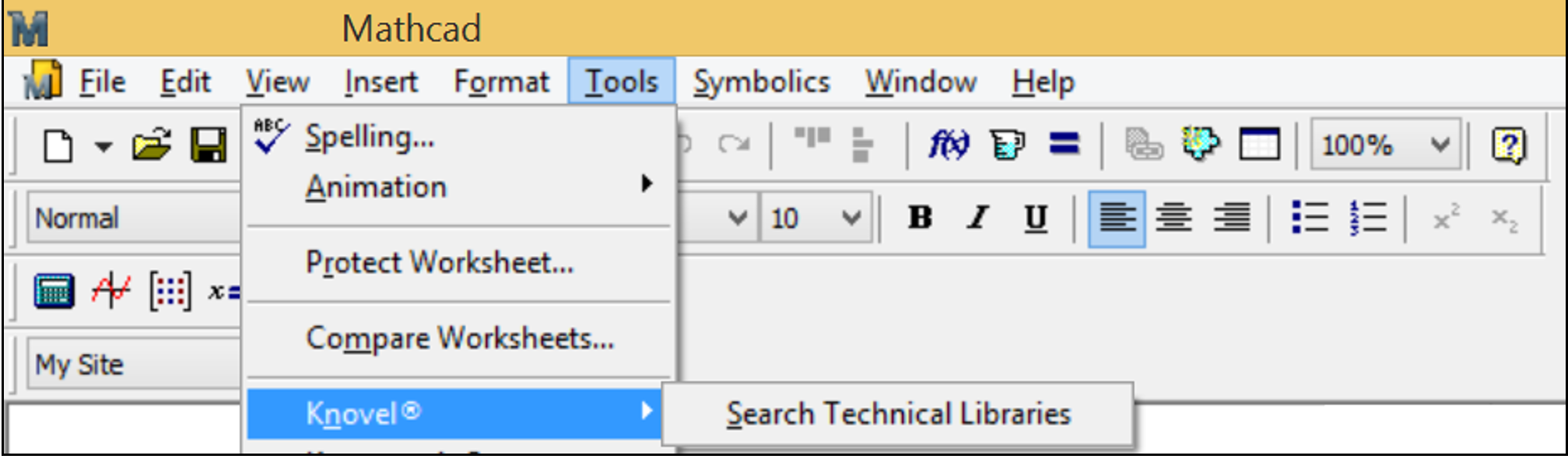
Fig. 5.8. Link to www.knovel.com from Mathcad 15
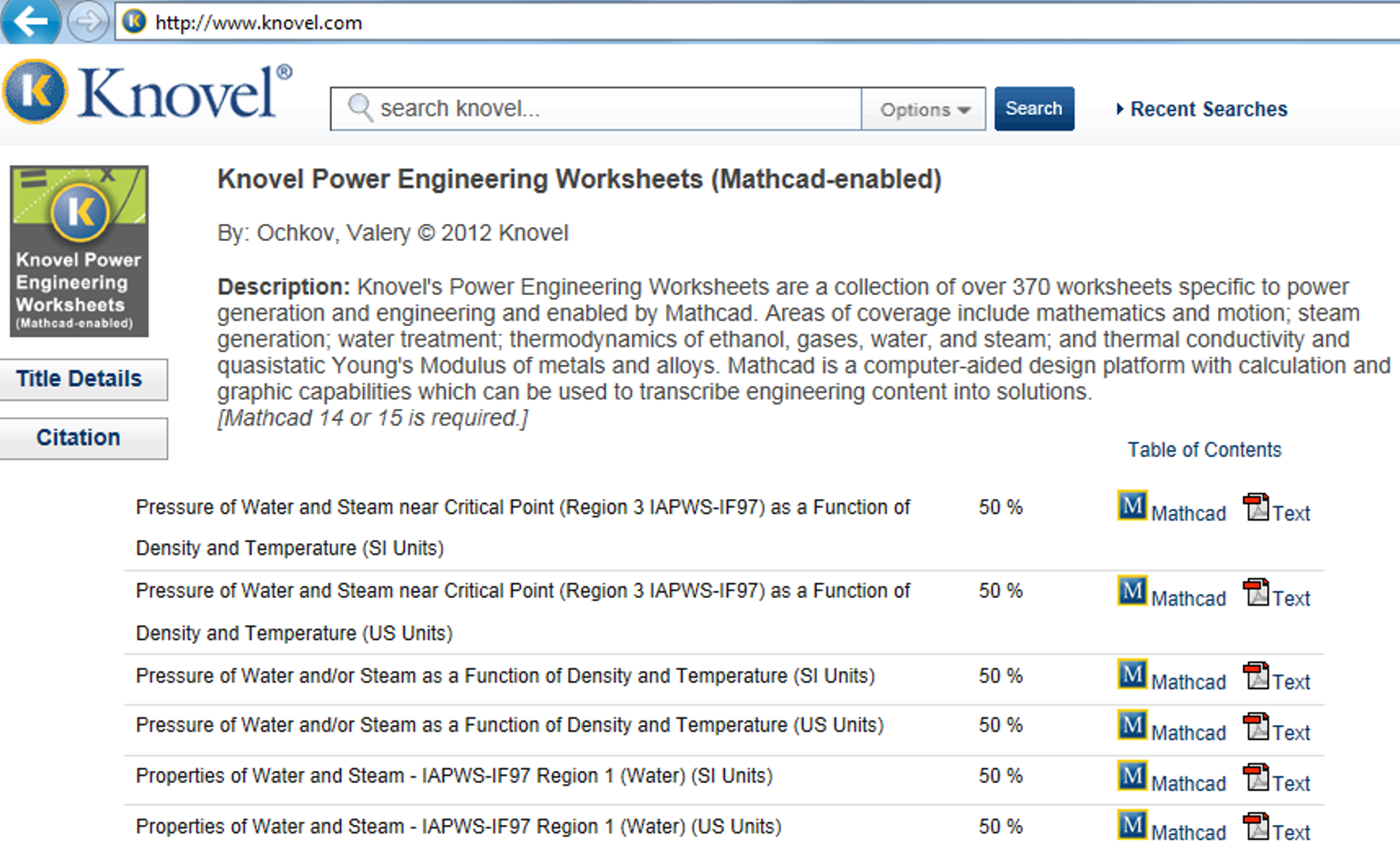
Fig. 5.9. Authoring Mathcad-calculations at Elsevier/Knovel web-sites
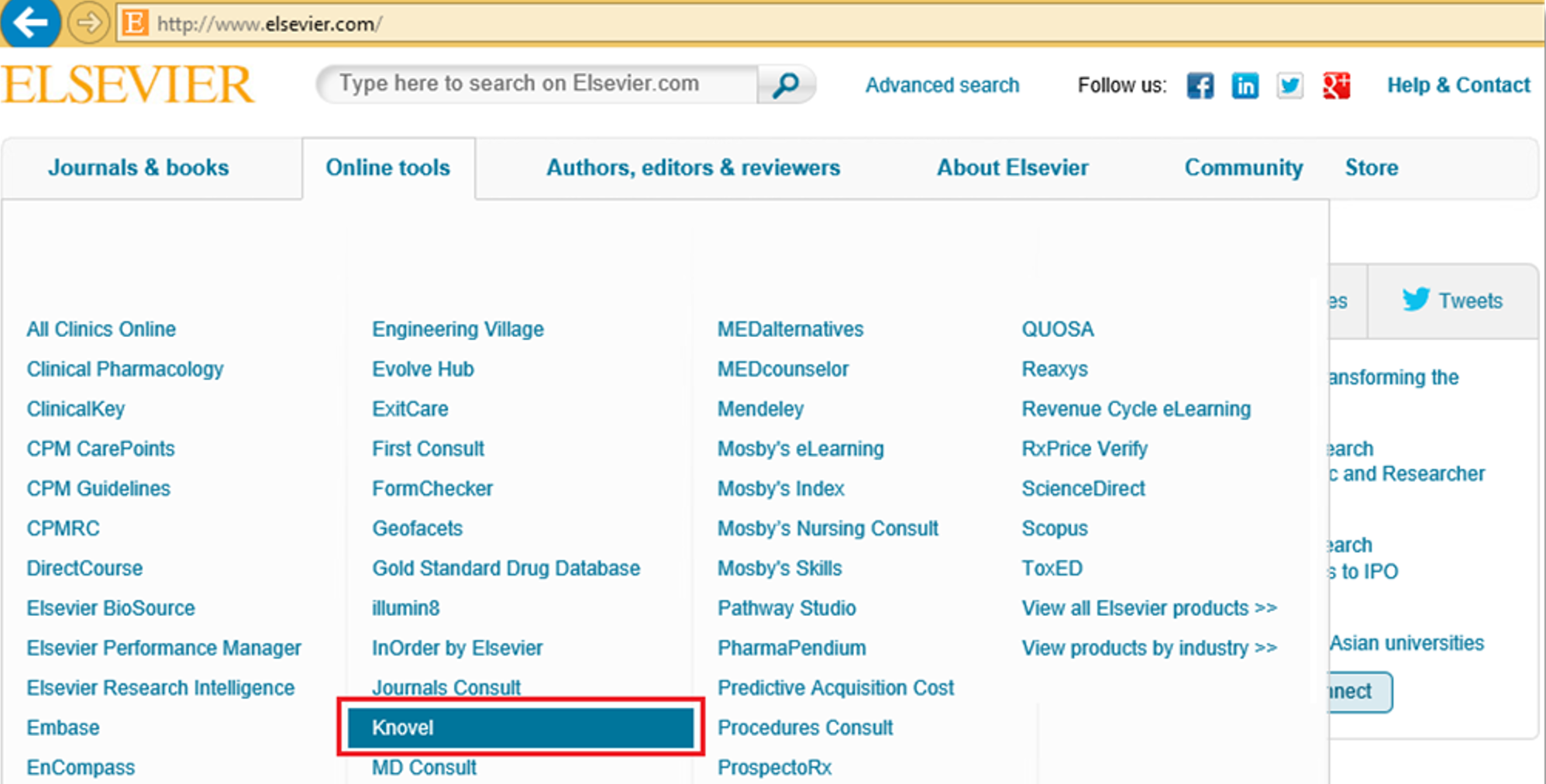
Fig. 5.10. Home page of e-publishing house Elsevier with a list of online tools
Fig. 5.10a. New home page of e-publishing house Elsevier with an information about Knovel
Fig. 5.11. Interactive tools from Knovel
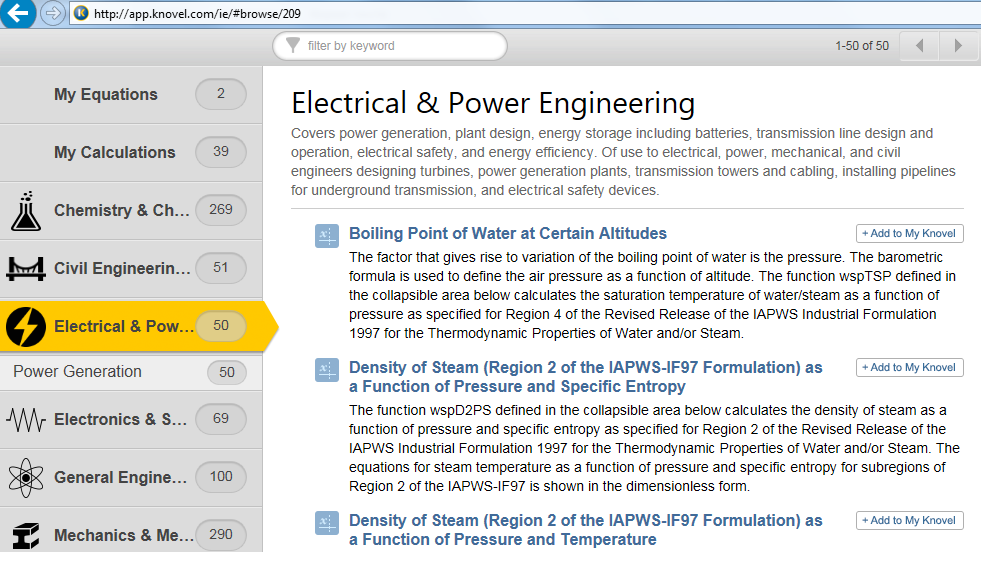
Fig. 5.12. Home page of Knovel’s Interactive Equations
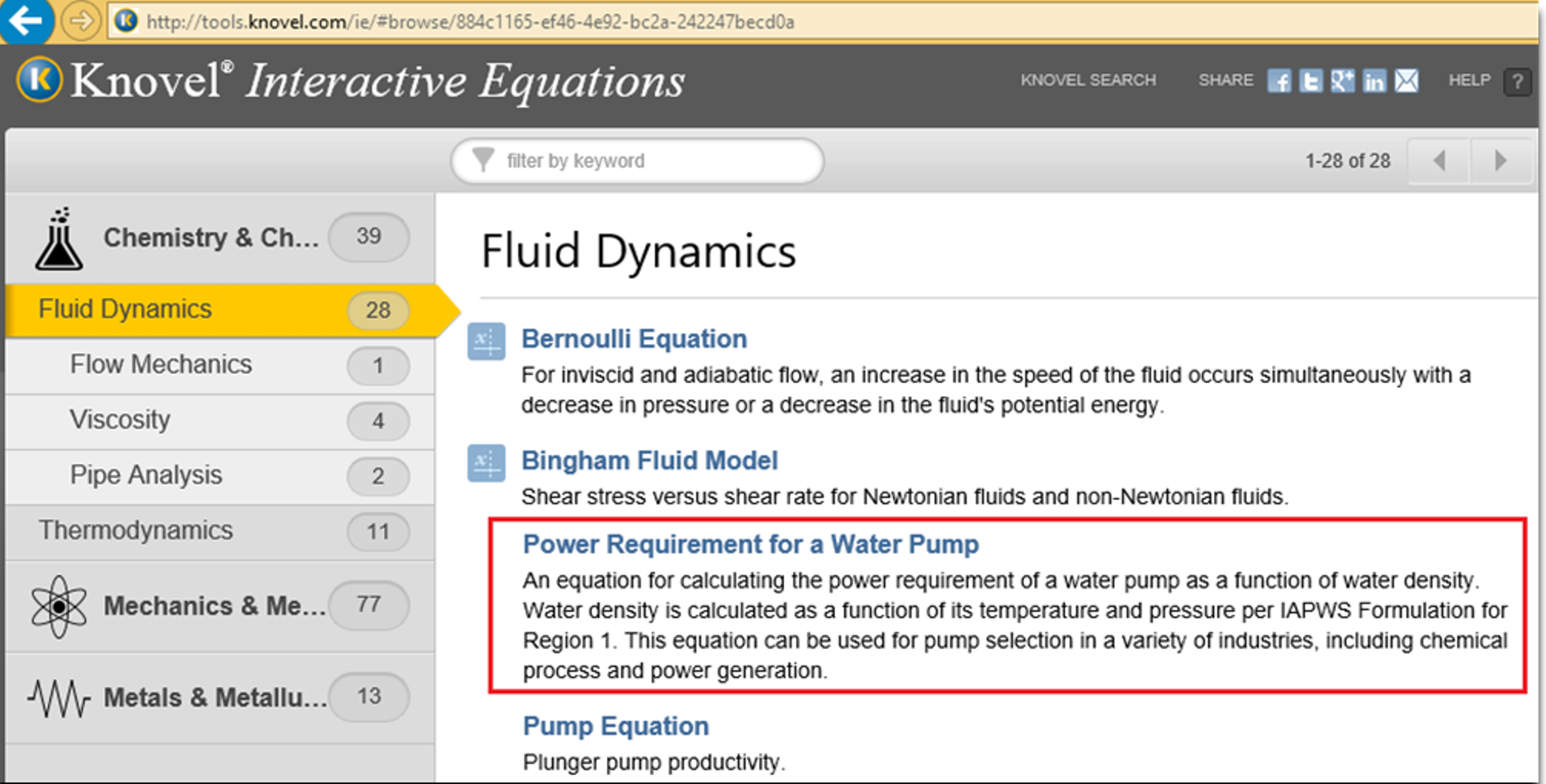
Fig. 5.13. Reference to pump power calculation in Interactive Equations of Knovel
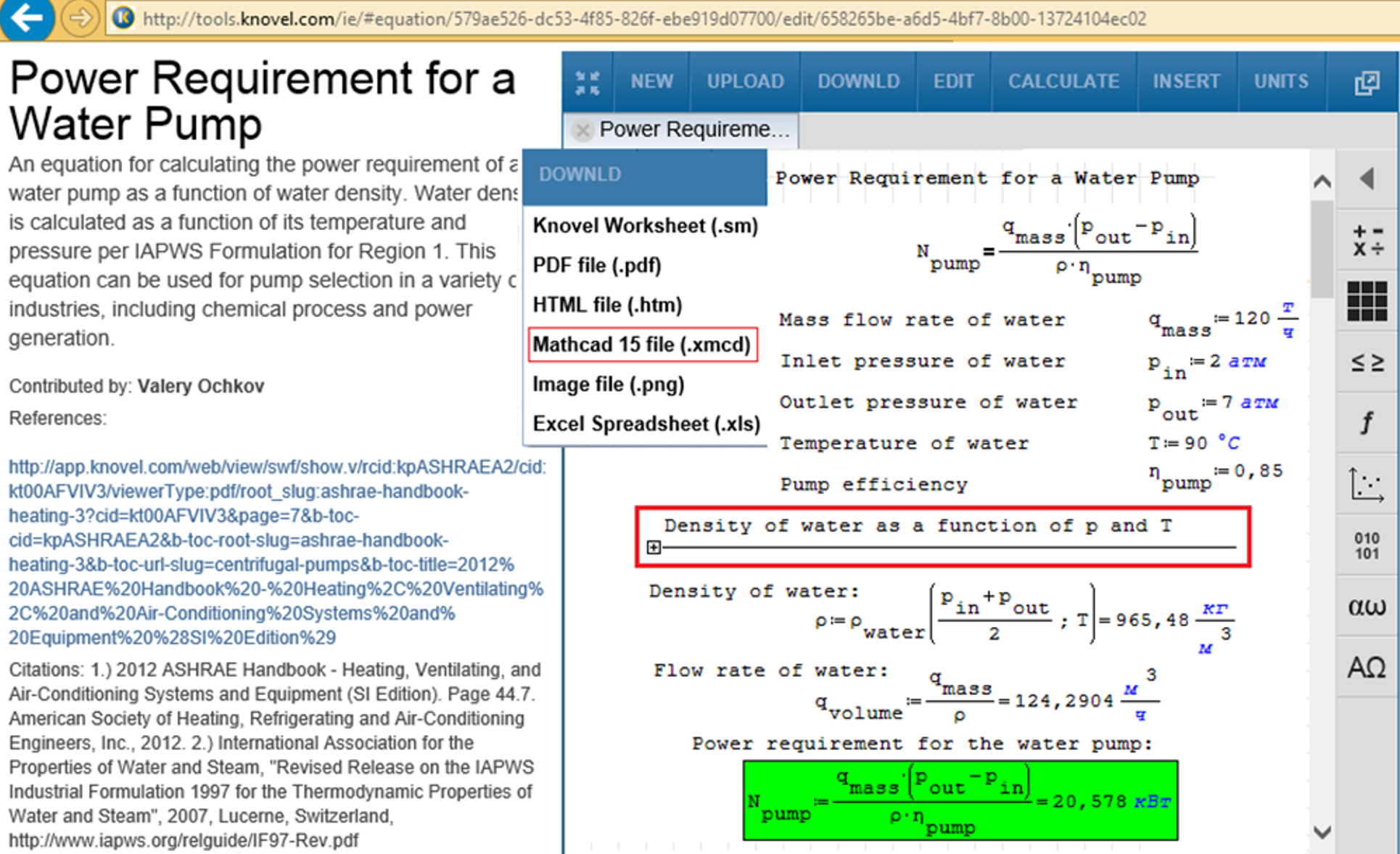
Fig. 5.14. Interactive calculation of pump power at Knovel’s web-site
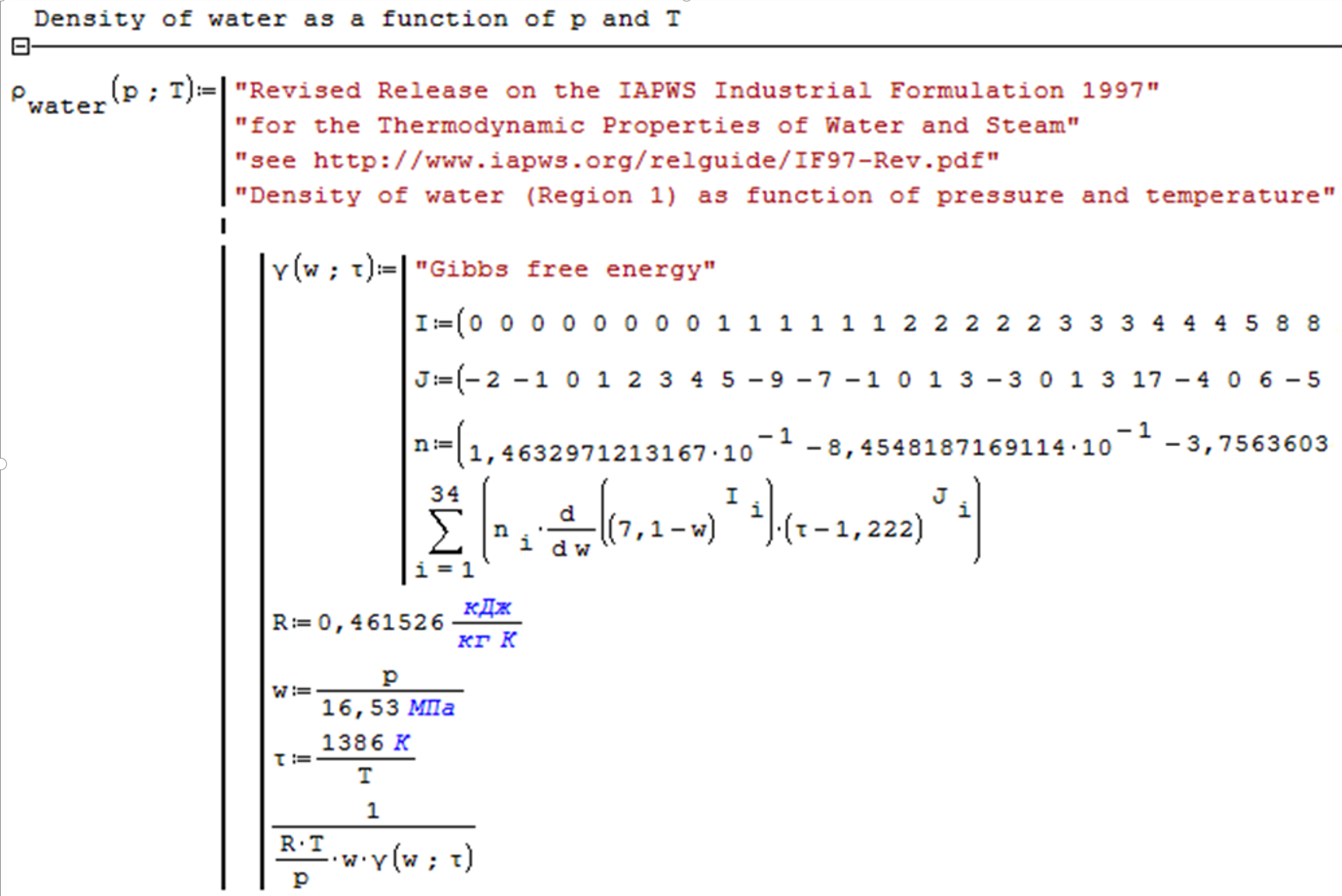
Fig. 5.15. Function of Knovel’s Interactive Equations converting water density (a part of the function is shown)
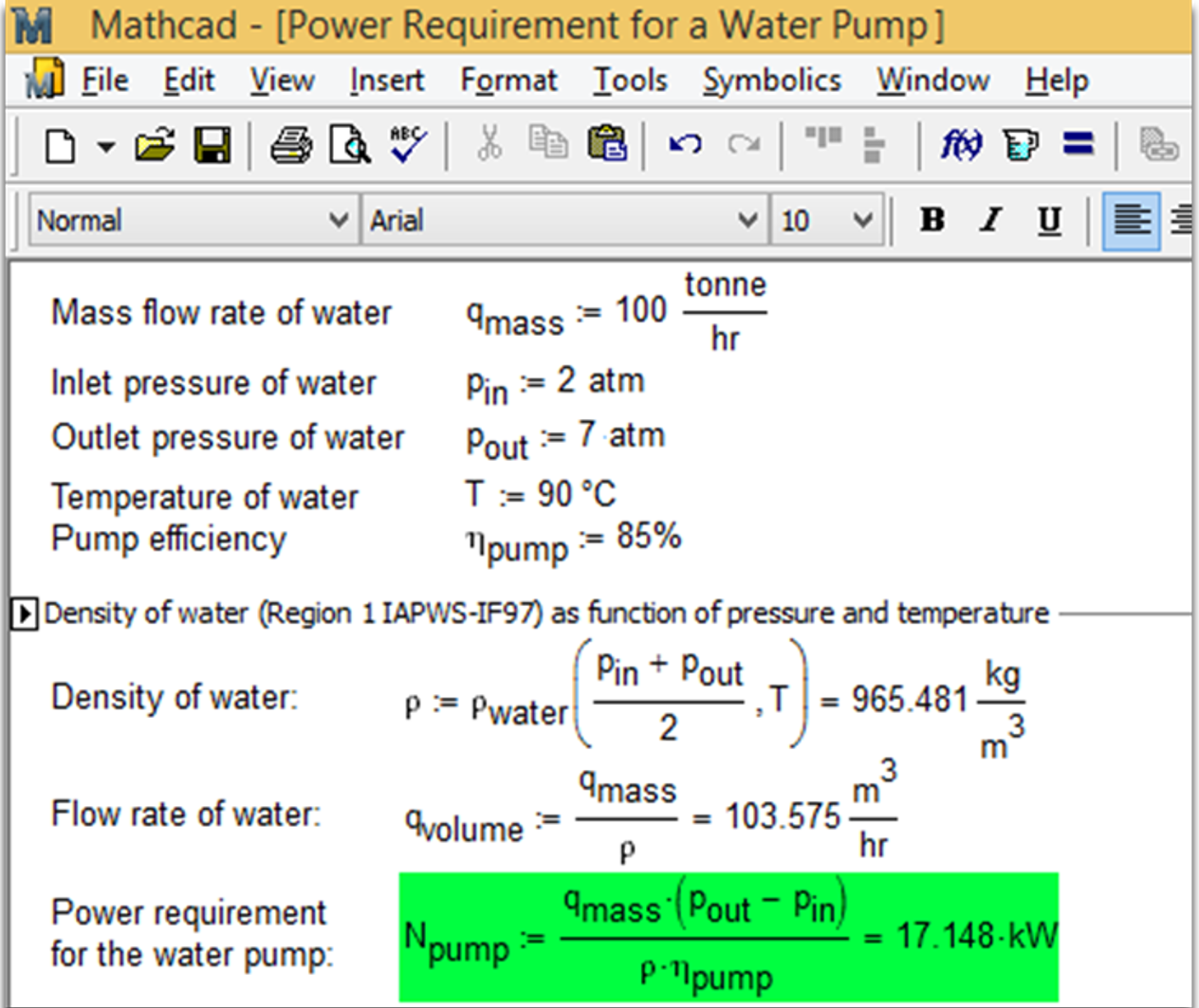
Fig. 5.16. Mathcad-calculation of pump power downloaded from Knovel’s Interactive Equations

Fig. 5.17. E-guide on thermal and physical properties of individual substances
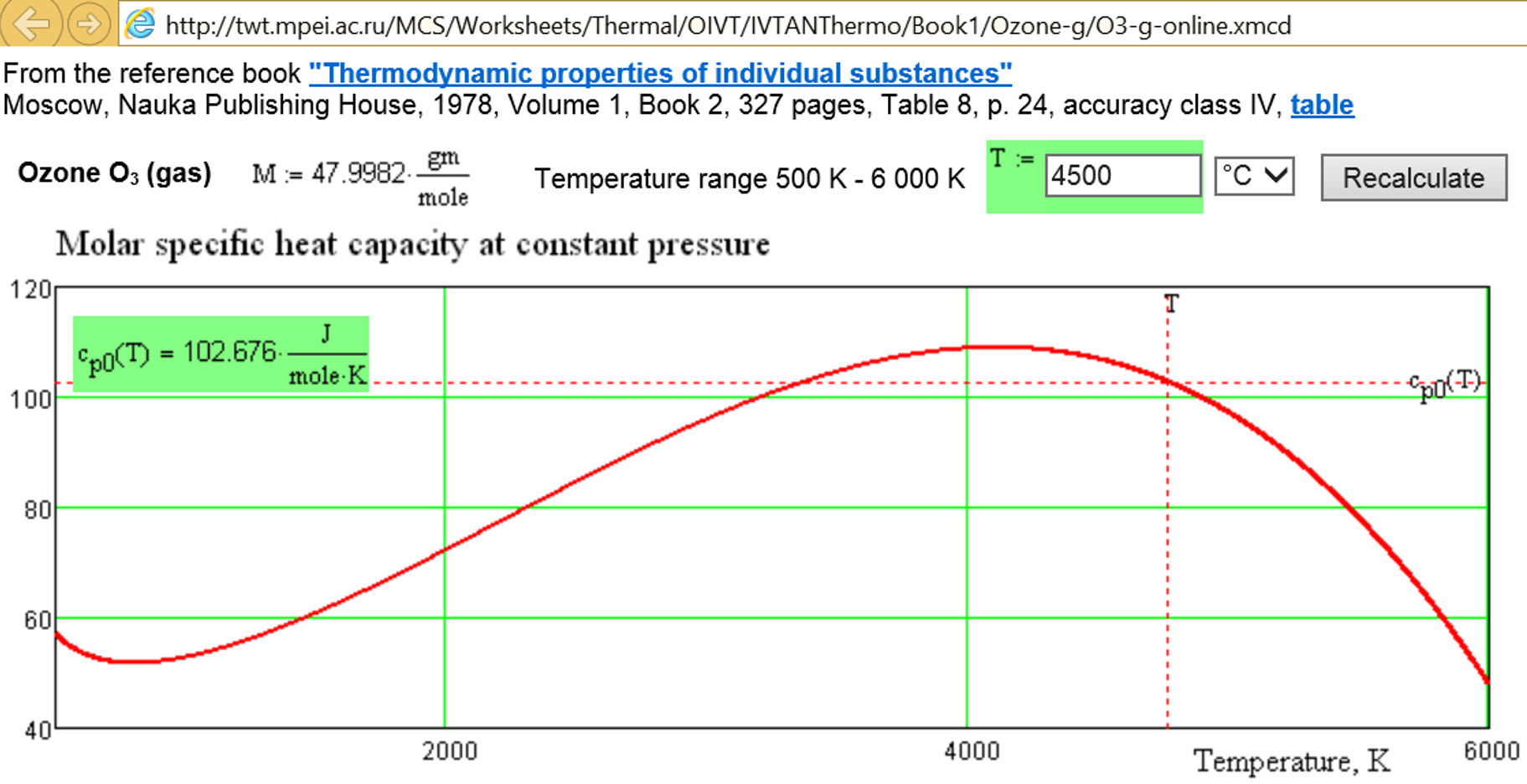
Fig. 5.18. Interactive network calculation of specific heat capacity of gaseous ozone
- Labels:
-
Other
- Tags:
- group discussion





