Community Tip - You can Bookmark boards, posts or articles that you'd like to access again easily! X
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Travel from home to school with... Fermat (сайт статьи "Путешествие от дома в школу по маршруту Ферма")
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Travel from home to school with... Fermat (сайт статьи "Путешествие от дома в школу по маршруту Ферма")
Figures and Mathcad- and Maple-sheets of the article
Рисунки и Mathcad & Maple документы статьи
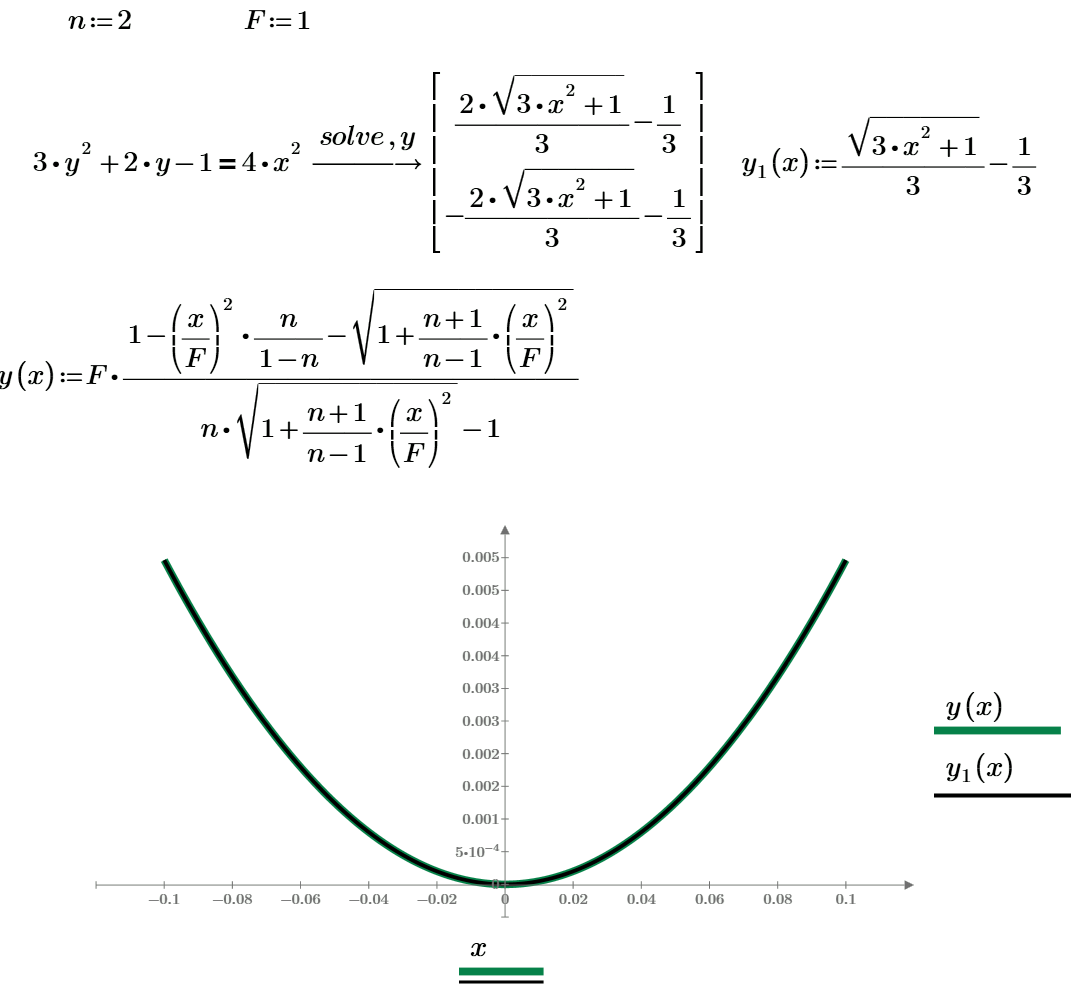
Рис. 1. Задача о беге по газону, пашне и асфальту: оптимизация
Fig. 1. The problem of running across the lawn, plowing and asphalt optimization
Проблемы, возникшие при решении этой задачи (Problems with this problem):
Why I cannot create a counter plot
One minimize problem - numerical and symbolical solutions
- Labels:
-
Other
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator

Рис. 2. Задача о беге по газону, пашне и асфальту: решение системы двух «оптических» уравнений
Fig. 2. The problem of running across the lawn, plowing and asphalt: the solution of the two "optical" equations
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Рис. 3. Физическое объяснение миража
ig. 3. The physical explanation of mirage
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
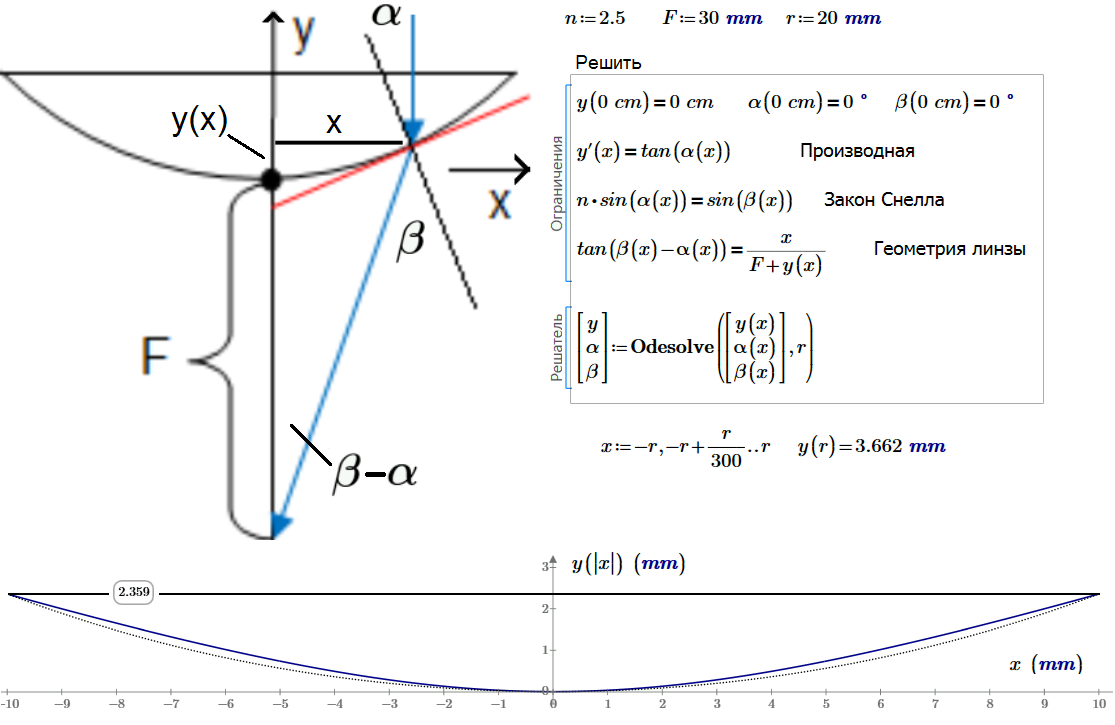
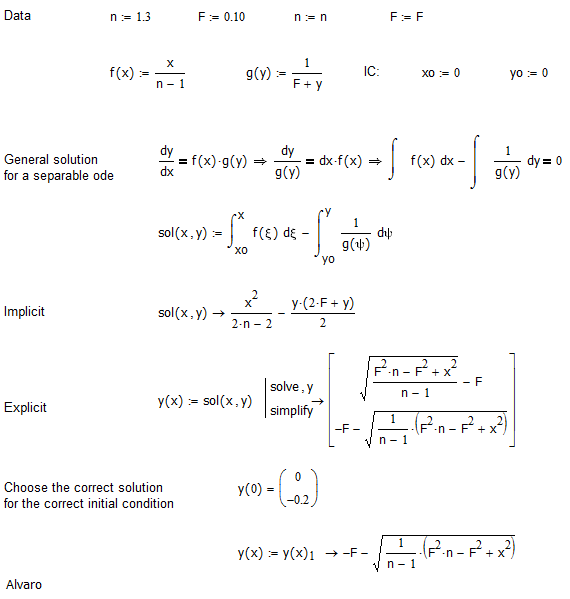
Рис. 4. Решение дифференциального уравнения линзы
Fig. 4. Solution of the lens of the differential equation
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator

Рис. 4. Численные и аналитические решения полного и упрощенного дифференциального уравнения линзы
Fig. 4. Numerical and analytical solutions of the full and simplified lens differential equation
Solution asymptote + odesolve
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator

Fig. 4a. Maple-solution of ODE (a bug in Maple)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Thanks, Alvaro!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Symbolic solution of system of ODE in Mathcad 11 (sic!) by Luc Meekes



- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
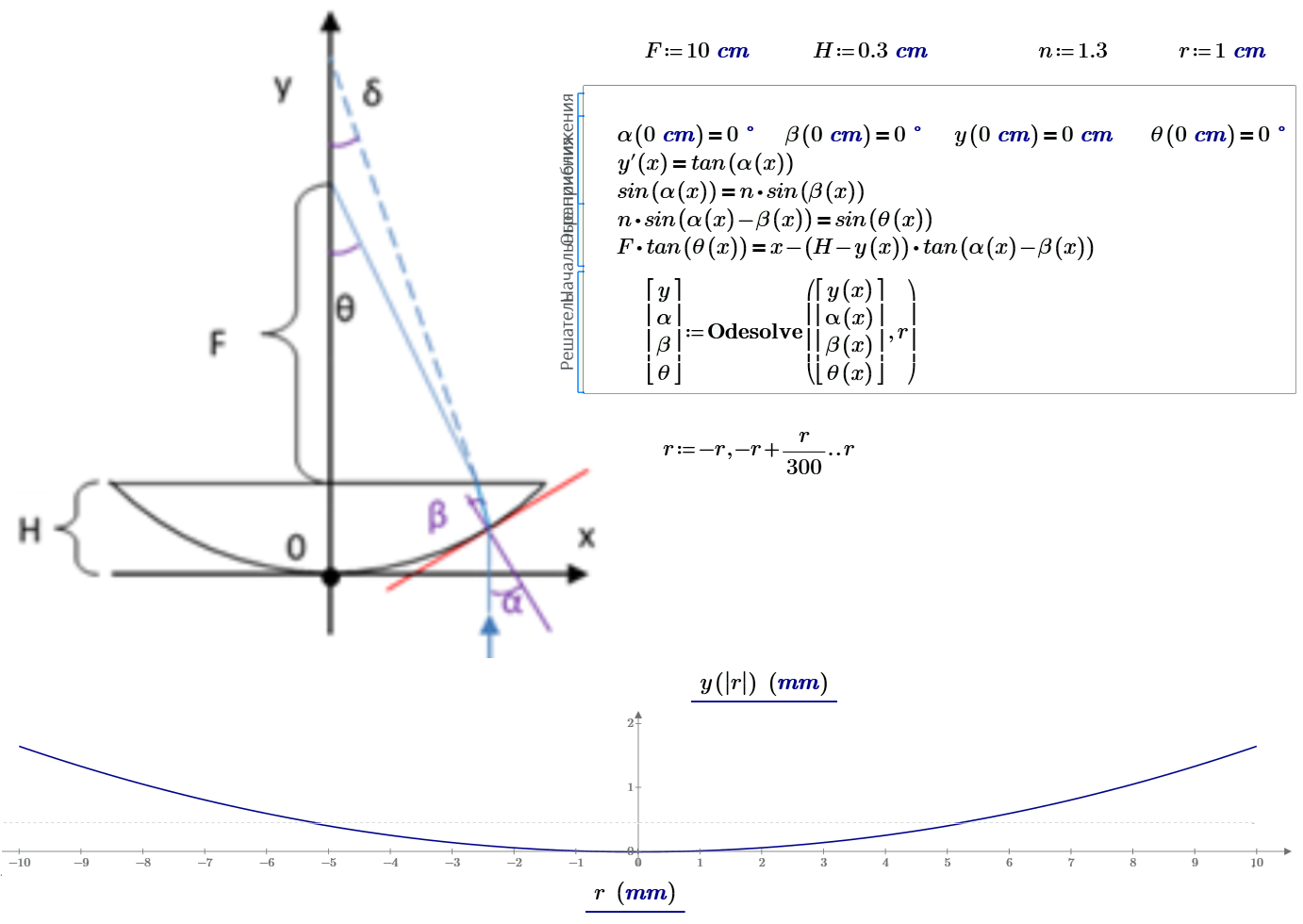
Рис. 4a. Решение дифференциального уравнения линзы (линзу перевернули)
Fig. 4a. Solution of the lens of the differential equation (a reverse lens)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
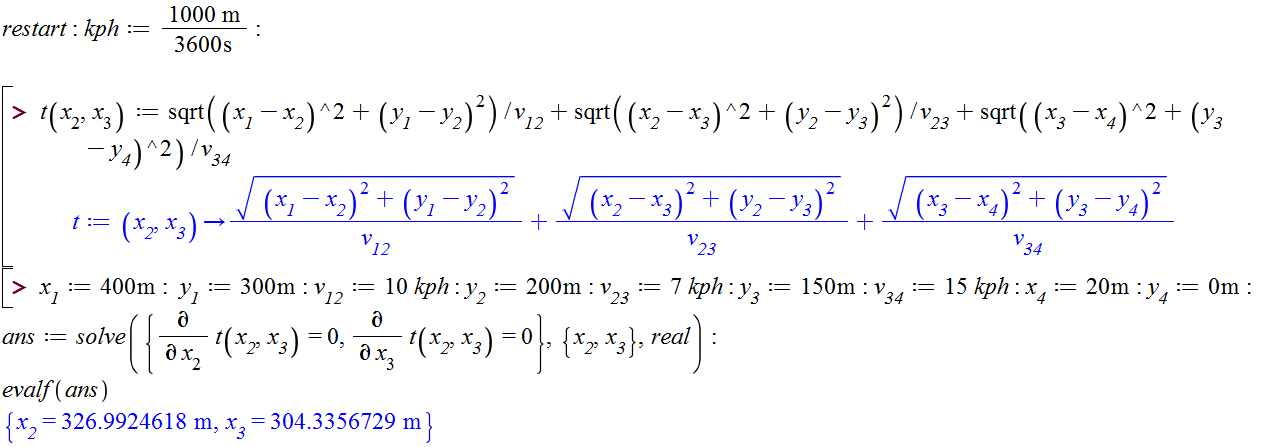
Рис. 2a. Maple solution of two equation
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
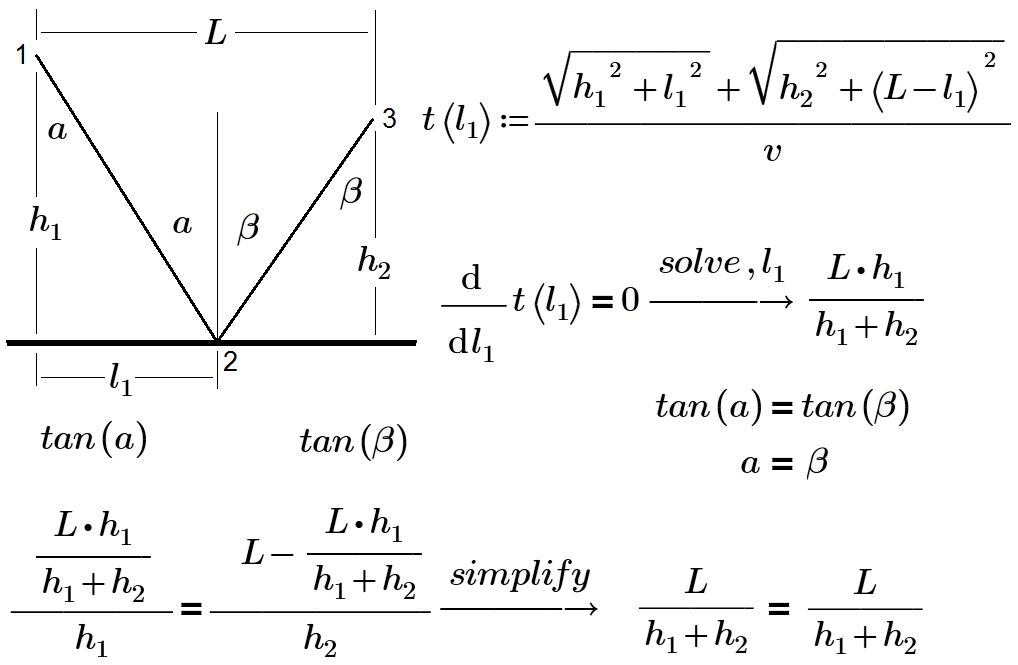
Рис. 5. Доказательство закона отражения Света
Сам файл с расчетом и обсуждение здесь Re: What is it the second root?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
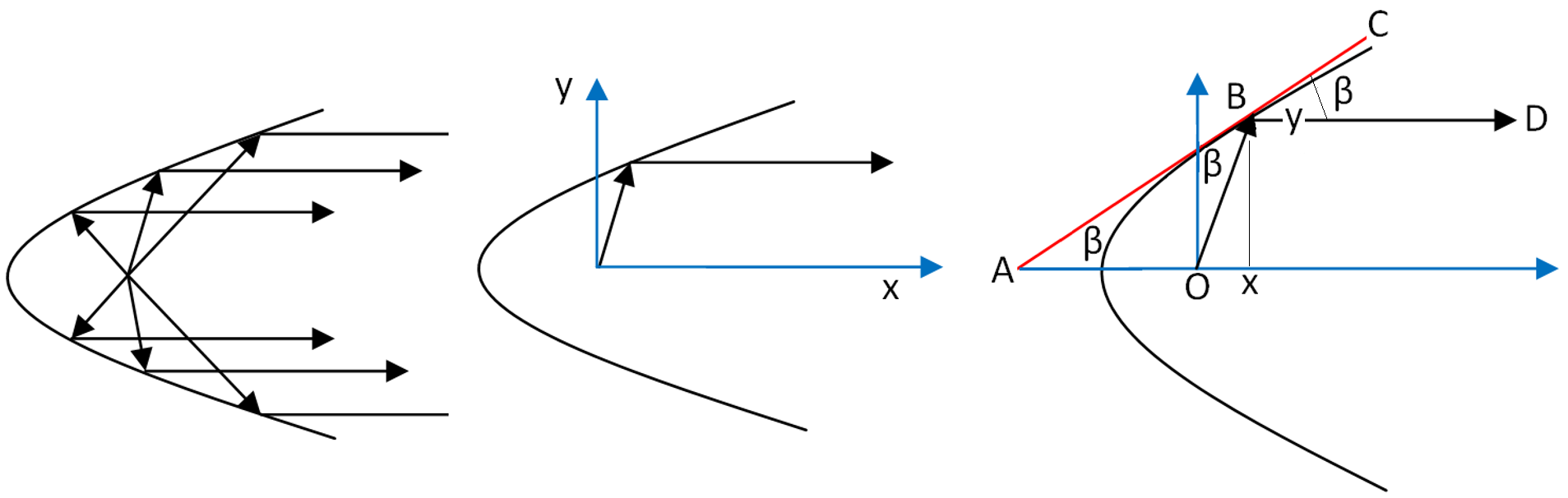
Рис. 6. Схема фокусирующего зеркала
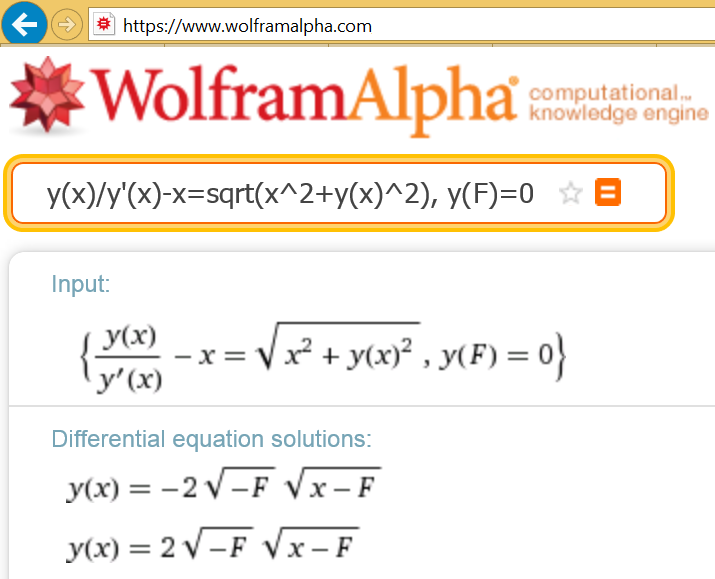
Рис. 7. Расчет формы зеркала, фокусирующего параллельный пучок света в точке
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
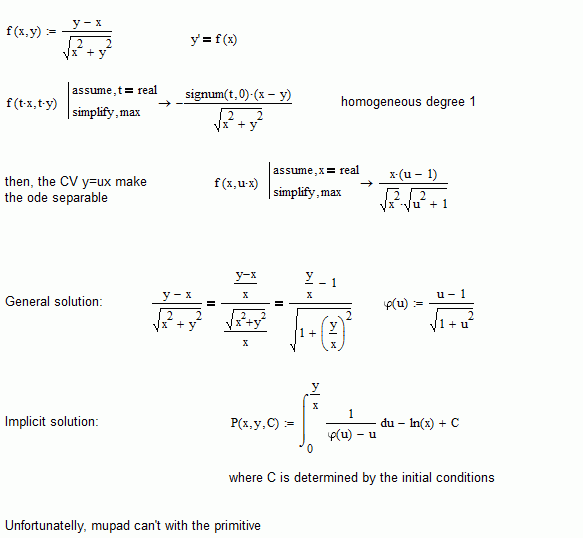
Homogeneus equation, but Mupad can't solve the primitive. Ah, me too, can't, by hand. Obviously, Mathematica can, but guess that for some change of variable, because the answer is very simple.
Best regards.
Alvaro.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Конические сечения (эллипс, парабола, гипербола) вообще обладают простыми, и, в то же время, удивительными свойствами. Лучи выходящие из фокуса "двухфокусных" сечений (эллипса и гиперболы) обязательно имеют продолжение во втором фокусе, независимо от того падают они внутри или снаружи эллипса и гиперболы. А лучи выходящие из фокуса параболы после отражения превращаются в параллельные лучи (также независимо от того внутри или снаружи параболы они падают). Глубоко уважаемый Crusoe Журнал Crusoe с применением этих свойств конических сечений провел увлекательное исследование на тему известнейшего произведения А.Н. Толстого "Гиперболоид инженера Гарина" в своем Третье зеркало.: crusoe и пришел к нетривиальному выводу!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Better in English
Conic sections (ellipse, parabola, hyperbola) generally have a simple and, at the same time, surprising properties. Beams exiting out of focus "bifocal" in cross section (ellipse and hyperbola) necessarily have continued in the second focus, whether they fall inside or outside the ellipse and hyperbola. After reflection the rays emerging from the focus of the parabola are converted into parallel beams (regardless of whether inside or outside the parabola they fall). Deeply respected Crusoe Crusoe Journal using these properties of conic sections had a fascinating study on the subject of the famous works of AN Tolstoy "hyperboloid of Engineer Garin" in its third mirror .: crusoe and came to the conclusion that a non-trivial!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
The variant of the article from 19/12/2016 in attach
Abstract.
The article considers the the solution of optimization problems as applied problems of reflection and refraction of light ray. Presented numerical and analytical solution of algebraic and differential quations lens and a focusing mirror in Mathcad.
It is shown how modern software tools can easily and gracefully olve optical problems. Analytically solved ordinary differential equation of a plano-convex lens.
It is emphasized that hyperbolical optical property, is not based on the laws of reflection, and on the law of light refraction. Formula was deduced for material of refractive index of a plano-convex lens with the same optical and geometrical focuses.
Keywords: reflection and refraction of light, optical path, Fermat's principle, tautochronism principle, Snellius law, Mathcad package, hyperbole, parabola.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
Second optical property of hyperbola - minimize and animation
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Notify Moderator